Periodic table of the elements on Mars answer key unlocks a captivating journey into the elemental composition of the Red Planet. This comprehensive guide unravels the significance of the periodic table in understanding the elements found on Mars, providing a thorough list of identified elements, their atomic numbers, and symbols.
Delving into the similarities and differences between the periodic tables of Mars and Earth, this exploration sets the stage for a deeper understanding of the Martian landscape.
Beyond the mere listing of elements, this guide delves into the abundance and distribution of elements on Mars, shedding light on their relative proportions and the geological processes that have shaped their distribution. Specific regions where elements are concentrated are identified, providing valuable insights into the planet’s geological history.
The chemical composition of Martian soil and rocks is meticulously analyzed, highlighting the presence of major and trace elements. The mineralogy of Martian rocks and minerals, including their crystal structures and chemical formulas, is thoroughly discussed, offering a glimpse into the planet’s geological evolution.
Periodic Table of the Elements on Mars
The periodic table of elements is a fundamental tool for understanding the chemical composition of Mars. It provides a systematic arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties. By studying the periodic table of Mars, scientists can gain insights into the planet’s geological history, mineral composition, and potential resources.
Comprehensive List of Elements Identified on Mars, Periodic table of the elements on mars answer key
- Hydrogen (H)
- Helium (He)
- Carbon (C)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
- Neon (Ne)
- Sodium (Na)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Silicon (Si)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Sulfur (S)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Argon (Ar)
- Potassium (K)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Scandium (Sc)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Vanadium (V)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Manganese (Mn)
- Iron (Fe)
- Cobalt (Co)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Copper (Cu)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Gallium (Ga)
- Germanium (Ge)
- Arsenic (As)
- Selenium (Se)
- Bromine (Br)
- Krypton (Kr)
- Rubidium (Rb)
- Strontium (Sr)
- Yttrium (Y)
- Zirconium (Zr)
- Niobium (Nb)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Technetium (Tc)
- Ruthenium (Ru)
- Rhodium (Rh)
- Palladium (Pd)
- Silver (Ag)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Indium (In)
- Tin (Sn)
- Antimony (Sb)
- Tellurium (Te)
- Iodine (I)
- Xenon (Xe)
- Cesium (Cs)
- Barium (Ba)
- Lanthanum (La)
- Cerium (Ce)
- Praseodymium (Pr)
- Neodymium (Nd)
- Promethium (Pm)
- Samarium (Sm)
- Europium (Eu)
- Gadolinium (Gd)
- Terbium (Tb)
- Dysprosium (Dy)
- Holmium (Ho)
- Erbium (Er)
- Thulium (Tm)
- Ytterbium (Yb)
- Lutetium (Lu)
- Hafnium (Hf)
- Tantalum (Ta)
- Tungsten (W)
- Rhenium (Re)
- Osmium (Os)
- Iridium (Ir)
- Platinum (Pt)
- Gold (Au)
- Mercury (Hg)
- Thallium (Tl)
- Lead (Pb)
- Bismuth (Bi)
- Polonium (Po)
- Astatine (At)
- Radon (Rn)
- Francium (Fr)
- Radium (Ra)
- Actinium (Ac)
- Thorium (Th)
- Protactinium (Pa)
- Uranium (U)
- Neptunium (Np)
- Plutonium (Pu)
- Americium (Am)
- Curium (Cm)
- Berkelium (Bk)
- Californium (Cf)
- Einsteinium (Es)
- Fermium (Fm)
- Mendelevium (Md)
- Nobelium (No)
- Lawrencium (Lr)
- Rutherfordium (Rf)
- Dubnium (Db)
- Seaborgium (Sg)
- Bohrium (Bh)
- Hassium (Hs)
- Meitnerium (Mt)
- Darmstadtium (Ds)
- Roentgenium (Rg)
- Copernicium (Cn)
- Nihonium (Nh)
- Flerovium (Fl)
- Moscovium (Mc)
- Livermorium (Lv)
- Tennessine (Ts)
- Oganesson (Og)
Similarities and Differences between the Periodic Table of Mars and Earth
The periodic table of Mars shares many similarities with that of Earth, indicating a common origin and chemical composition. However, there are also some notable differences, reflecting the unique geological history and environmental conditions of each planet.
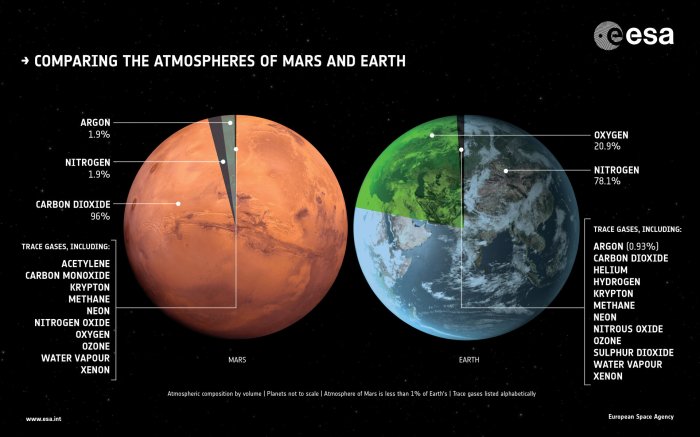
One key difference is the abundance of certain elements. For example, Mars has a higher concentration of iron than Earth, contributing to its reddish color. Conversely, Mars has lower levels of volatile elements such as nitrogen and carbon, which are essential for life as we know it.
Another difference is the presence of certain elements on Mars that are not found on Earth. For example, the Martian atmosphere contains small amounts of argon-36, a radioactive isotope that is produced by the decay of potassium-40. This suggests that Mars once had a thicker atmosphere with higher levels of potassium.
Key Questions Answered: Periodic Table Of The Elements On Mars Answer Key
What is the significance of the periodic table in understanding the elements found on Mars?
The periodic table provides a systematic framework for organizing and understanding the chemical elements, including those found on Mars. It allows scientists to predict the properties and behavior of elements based on their position in the table, aiding in the identification and analysis of elements present on the Red Planet.
How does the periodic table of Mars differ from that of Earth?
While the periodic table of Mars shares many similarities with that of Earth, there are some notable differences. Mars has a lower abundance of volatile elements, such as hydrogen and helium, due to its smaller size and weaker gravitational pull.
Additionally, the relative proportions of some elements, such as iron and magnesium, differ between the two planets, reflecting variations in their geological histories.
What are the potential resources for future exploration on Mars?
Mars holds a wealth of potential resources for future human missions. Elements such as oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon are essential for life support and can be extracted from the Martian atmosphere or soil. Additionally, Mars is rich in minerals containing valuable elements like iron, titanium, and aluminum, which could be utilized for construction, manufacturing, and other industrial purposes.