Embark on an enlightening journey with our energy frequency wavelength worksheet answer key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the enigmatic relationship between energy, frequency, and wavelength. Delving into the core concepts of physics, this resource unravels the intricacies of the electromagnetic spectrum, wave properties, and wave interactions, empowering you with a profound understanding of these fundamental phenomena.
As we delve into the depths of this worksheet, we’ll explore real-world applications, unravel the mysteries of wave behavior, and equip you with the tools to solve complex wave-related problems. Prepare to immerse yourself in a world of energy and waves, where knowledge and clarity converge.
1. Energy Frequency and Wavelength: Energy Frequency Wavelength Worksheet Answer Key
Energy, frequency, and wavelength are three interrelated concepts in physics. Energy is the ability to do work, and it can be expressed in various units, such as joules or electron volts. Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time, and it is typically expressed in hertz (Hz).
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave, and it is typically expressed in meters (m).
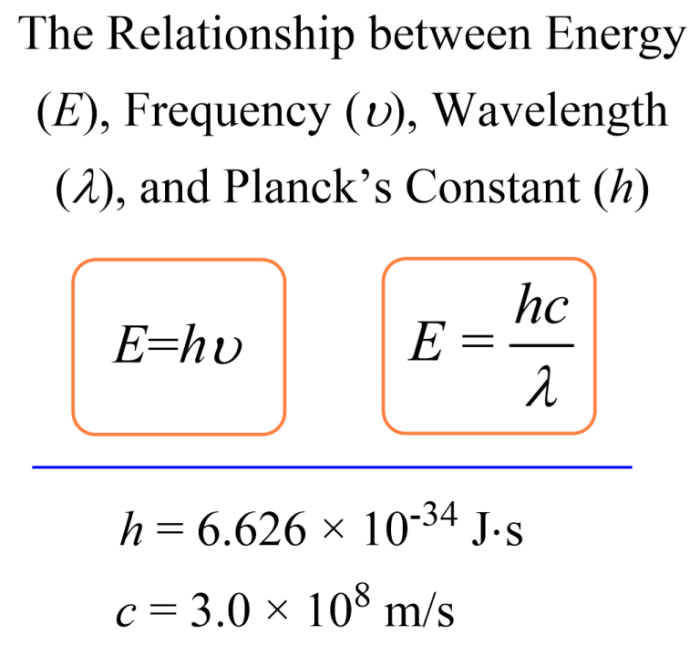
The relationship between energy, frequency, and wavelength can be expressed by the following equation:
“`E = hf“`
where:
* E is energy
- h is Planck’s constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J s)
- f is frequency
This equation shows that the energy of a photon is directly proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength.
This relationship is applied in various real-world scenarios. For example, it is used in the design of antennas, which convert electromagnetic energy into radio waves. It is also used in the operation of lasers, which produce highly focused beams of light.
The units of measurement for energy, frequency, and wavelength are as follows:
* Energy: joules (J)
Frequency
hertz (Hz)
Wavelength
meters (m)
Key Questions Answered
What is the relationship between energy, frequency, and wavelength?
Energy, frequency, and wavelength are inversely related. As energy increases, frequency increases and wavelength decreases, and vice versa.
What are the different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays, each with its distinct frequency and wavelength range.
How do waves interact with each other?
Waves can interact through reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference. Reflection occurs when a wave bounces off a surface, refraction when it changes direction upon entering a new medium, diffraction when it spreads out after passing through an aperture, and interference when two or more waves combine to produce a new wave pattern.